iFluor® 560 maleimide
iFluor® 560 maleimide is a thiol-reactive orange fluorophore with superior brightness compared to Cy3 that enables site-specific protein labeling at cysteine residues for advanced imaging applications.
- Superior Solubility: Enhanced aqueous solubility for efficient biomolecule conjugation
- High Photostability: High quantum yield and stability facilitate the detection of low-abundance targets with greater sensitivity
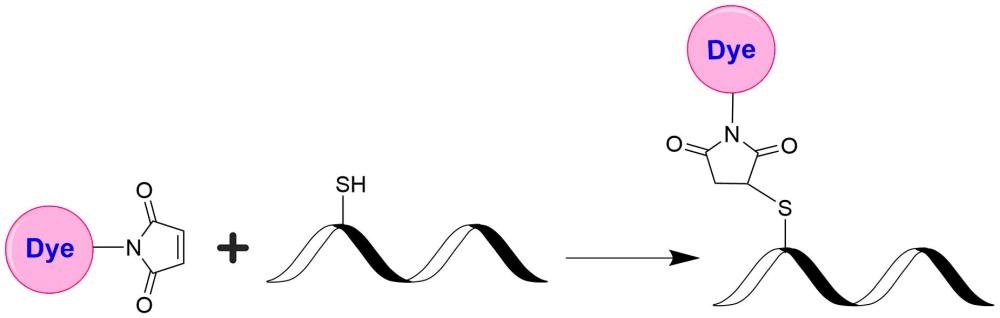
- Versatile Conjugation: Maleimide chemistry enables efficient and stable labeling of thiol groups on proteins, antibodies, and oligonucleotide thiophosphates
- Spectrally Similar Dyes: Cy3, Cy3B

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 71684 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1282.51 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.0482 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.069 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 120000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 560 |
| Emission (nm) | 571 |
| Quantum yield | 0.57 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 16, 2026

