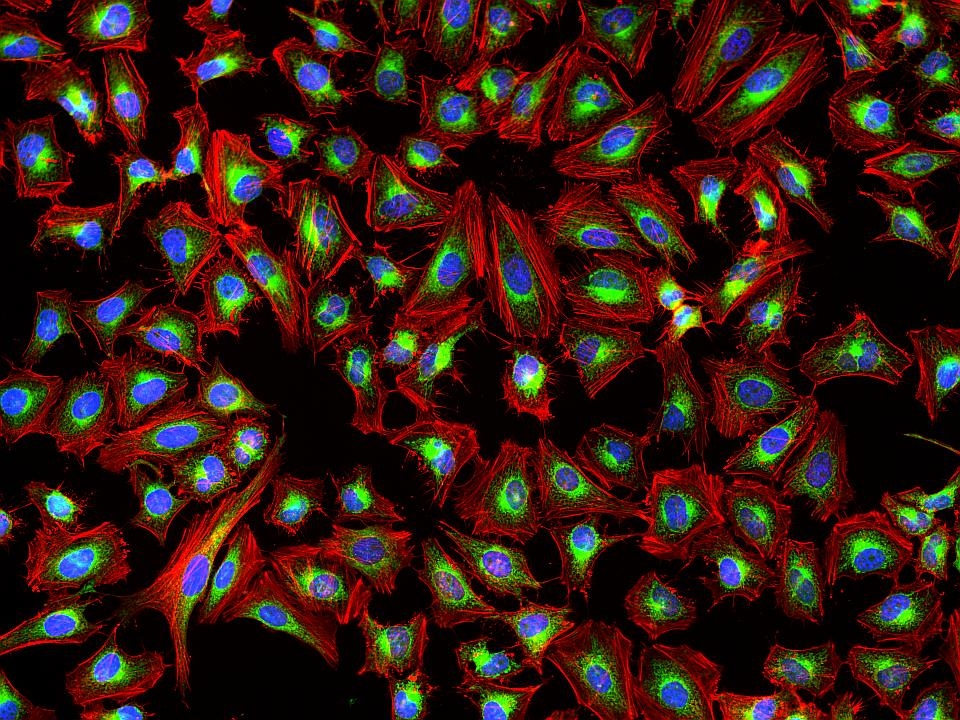
Phalloidin Conjugates
iFluor® 647
This deep red fluorescent phalloidin conjugate (equivalent to Alexa Fluor® 647-labeled phalloidin) selectively binds to F-actins. Used at nanomolar concentrations, phalloidin derivatives are convenient probes for labeling, identifying and quantitating F-actins in formaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized tissue sections, cell cultures or cell-free experiments. Phalloidin binds to actin filaments much more tightly than to actin monomers, leading to a decrease in the rate constant for the dissociation of actin subunits from filament ends, essentially stabilizing actin filaments through the prevention of filament depolymerization. Moreover, phalloidin is found to inhibit the ATP hydrolysis activity of F-actin. Phalloidin functions differently at various concentrations in cells. When introduced into the cytoplasm at low concentrations, phalloidin recruits the less polymerized forms of cytoplasmic actin as well as filamin into stable "islands" of aggregated actin polymers, yet it does not interfere with stress fibers, i.e. thick bundles of microfilaments. The property of phalloidin is a useful tool for investigating the distribution of F-actin in cells by labeling phalloidin with fluorescent analogs and using them to stain actin filaments for light microscopy. Fluorescent derivatives of phalloidin have turned out to be enormously useful in localizing actin filaments in living or fixed cells as well as for visualizing individual actin filaments in vitro. Fluorescent phalloidin derivatives have been used as an important tool in the study of actin networks at high resolution. AAT Bioquest offers a variety of fluorescent phalloidin derivatives with different colors for multicolor imaging applications.
Example protocol
AT A GLANCE
Protocol Summary
- Prepare samples in microplate wells
- Remove liquid from samples in the plate
- Add Phalloidin-iFluor™ 647 Conjugate solution (100 μL/well)
- Stain the cells at room temperature for 20 to 90 minutes
- Wash the cells
- Examine the specimen under microscope with Cy5 filter
Storage and Handling Conditions
The solution should be stable for at least 6 months if store at -20 °C. Protect the fluorescent conjugates from light, and avoid freeze/thaw cycles.Note Phalloidin is toxic, although the amount of toxin present in a vial could be lethal only to a mosquito (LD50 of phalloidin = 2 mg/kg), it should be handled with care.
PREPARATION OF STOCK SOLUTIONS
Unless otherwise noted, all unused stock solutions should be divided into single-use aliquots and stored at -20 °C after preparation. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Phalloidin-iFluor™ 647 Conjugate stock solution
Add 30 µL of DMSO into the powder and mix well.PREPARATION OF WORKING SOLUTION
Phalloidin-iFluor™ 647 Conjugate working solution
Add 1 µL of Phalloidin-iFluor™ 647 Conjugate solution to 1 mL of PBS with 1% BSA.Note The stock solution of phalloidin conjugate should be aliquoted and stored at -20 °C. protected from light.
Note Different cell types might be stained differently. The concentration of phalloidin conjugate working solution should be prepared accordingly.
SAMPLE EXPERIMENTAL PROTOCOL
Stain the cells
- Perform formaldehyde fixation. Incubate cells with 3.0–4.0 % formaldehyde in PBS at room temperature for 10–30 minutes.
Note Avoid any methanol containing fixatives since methanol can disrupt actin during the fixation process. The preferred fixative is methanol-free formaldehyde. - Rinse the fixed cells 2–3 times in PBS.
- Optional: Add 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS into fixed cells for 3 to 5 minutes to increase permeability. Rinse the cells 2–3 times in PBS.
- Add 100 μL/well (96-well plate) of Phalloidin-iFluor™ 647 Conjugate working solution into the fixed cells, and stain the cells at room temperature for 20 to 90 minutes.
- Rinse cells gently with PBS 2 to 3 times to remove excess phalloidin conjugate before plating, sealing and imaging under microscope with Cy5 filter set.
Spectrum
Alternative formats
| Name | Conjugate |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 488 Conjugate | iFluor 488 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 647 Conjugate | iFluor 647 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 594 Conjugate | iFluor 594 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 555 Conjugate | iFluor 555 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 633 Conjugate | iFluor 633 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 532 Conjugate | iFluor 532 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 405 Conjugate | iFluor 405 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 514 Conjugate | iFluor 514 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 350 Conjugate | iFluor 350 |
Show More (15) | |
Product family
| Name | Excitation (nm) | Emission (nm) | Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | Quantum yield | Correction Factor (260 nm) | Correction Factor (280 nm) |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 350 Conjugate | 345 | 450 | 200001 | 0.951 | 0.83 | 0.23 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 405 Conjugate | 403 | 427 | 370001 | 0.911 | 0.48 | 0.77 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 488 Conjugate | 491 | 516 | 750001 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.11 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 514 Conjugate | 511 | 527 | 750001 | 0.831 | 0.265 | 0.116 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 532 Conjugate | 537 | 560 | 900001 | 0.681 | 0.26 | 0.16 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 555 Conjugate | 557 | 570 | 1000001 | 0.641 | 0.23 | 0.14 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 594 Conjugate | 587 | 603 | 2000001 | 0.531 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 633 Conjugate | 640 | 654 | 2500001 | 0.291 | 0.062 | 0.044 |
| Phalloidin-iFluor® 680 Conjugate | 684 | 701 | 2200001 | 0.231 | 0.097 | 0.094 |
Show More (4) | ||||||
Citations
View all 151 citations: Citation Explorer
Cells proliferation on surfaces functionalized with amyloid beta peptide fibrils
Authors: Beregoi, Mihaela and Nistor, Sara and Ciobotaru, Iulia Corina and Nitescu, Andrei and Zgura, Irina and Bunea, Mihaela Cristina and Enculescu, Monica and Nedelcu, Liviu and Busuioc, Cristina and Enache, Teodor Adrian
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2025): 143160
Authors: Beregoi, Mihaela and Nistor, Sara and Ciobotaru, Iulia Corina and Nitescu, Andrei and Zgura, Irina and Bunea, Mihaela Cristina and Enculescu, Monica and Nedelcu, Liviu and Busuioc, Cristina and Enache, Teodor Adrian
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2025): 143160
Bacteria-Derived Extracellular Vesicle as A “Trojan Horse” for Selective M1 Macrophage-Targeting in A Multi-Cellular Entanglement Environment
Authors: Cai, Donglin and Li, Zhelun and Gao, Wendong and Mu, Yuqing and Liu, Jiaying and Zhang, Yufeng and Mei, Xiaohan and Quan, Jingjing and Xiao, Lan and Xiao, Yin
Journal: Advanced Functional Materials (2025): 2501459
Authors: Cai, Donglin and Li, Zhelun and Gao, Wendong and Mu, Yuqing and Liu, Jiaying and Zhang, Yufeng and Mei, Xiaohan and Quan, Jingjing and Xiao, Lan and Xiao, Yin
Journal: Advanced Functional Materials (2025): 2501459
Bi-allelic variants in three genes encoding distinct subunits of the vesicular AP-5 complex cause hereditary macular dystrophy
Authors: Kaminska, Karolina and Cancellieri, Francesca and Quinodoz, Mathieu and Moye, Abigail R and Bauwens, Miriam and Lin, Siying and Janeschitz-Kriegl, Lucas and Hayman, Tamar and Barber{\'a}n-Mart{\'\i}nez, Pilar and Schlaeger, Regina and others,
Journal: The American Journal of Human Genetics (2025)
Authors: Kaminska, Karolina and Cancellieri, Francesca and Quinodoz, Mathieu and Moye, Abigail R and Bauwens, Miriam and Lin, Siying and Janeschitz-Kriegl, Lucas and Hayman, Tamar and Barber{\'a}n-Mart{\'\i}nez, Pilar and Schlaeger, Regina and others,
Journal: The American Journal of Human Genetics (2025)
Arcyriaflavin A Alleviates Osteoporosis by Suppressing RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis
Authors: Zhu, Mengbo and Xu, Mingwei and Bertheloot, Damien and Brom, Victoria C and Sieberath, Alexander and Salber, Jochen and Welle, Kristian and Burger, Christof and Wirtz, Dieter C and Wang, Shaowei and others,
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2025): 2141
Authors: Zhu, Mengbo and Xu, Mingwei and Bertheloot, Damien and Brom, Victoria C and Sieberath, Alexander and Salber, Jochen and Welle, Kristian and Burger, Christof and Wirtz, Dieter C and Wang, Shaowei and others,
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2025): 2141
Integrin stimulation by collagen I at the progenitor stage accelerates maturation of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes
Authors: Barreto-Gamarra, Carlos and Domenech, Maribella
Journal: Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (2025)
Authors: Barreto-Gamarra, Carlos and Domenech, Maribella
Journal: Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (2025)
References
View all 127 references: Citation Explorer
Phalloidin perturbs the interaction of human non-muscle myosin isoforms 2A and 2C1 with F-actin
Authors: Diensthuber RP, Muller M, Heissler SM, Taft MH, Chizhov I, Manstein DJ.
Journal: FEBS Lett (2011): 767
Authors: Diensthuber RP, Muller M, Heissler SM, Taft MH, Chizhov I, Manstein DJ.
Journal: FEBS Lett (2011): 767
Improved penile histology by phalloidin stain: circular and longitudinal cavernous smooth muscles, dual-endothelium arteries, and erectile dysfunction-associated changes
Authors: Lin G, Qiu X, F and el TM, Albersen M, Wang Z, Lue TF, Lin CS.
Journal: Urology (2011): 970 e1
Authors: Lin G, Qiu X, F and el TM, Albersen M, Wang Z, Lue TF, Lin CS.
Journal: Urology (2011): 970 e1
pH-(low)-insertion-peptide (pHLIP) translocation of membrane impermeable phalloidin toxin inhibits cancer cell proliferation
Authors: An M, Wijesinghe D, Andreev OA, Reshetnyak YK, Engelman DM.
Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010): 20246
Authors: An M, Wijesinghe D, Andreev OA, Reshetnyak YK, Engelman DM.
Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010): 20246
Labeling cytoskeletal F-actin with rhodamine phalloidin or fluorescein phalloidin for imaging
Authors: Chazotte B., undefined
Journal: Cold Spring Harb Protoc (2010): pdb prot4947
Authors: Chazotte B., undefined
Journal: Cold Spring Harb Protoc (2010): pdb prot4947
Protective effect of bile acid derivatives in phalloidin-induced rat liver toxicity
Authors: Herraez E, Macias RI, Vazquez-Tato J, Hierro C, Monte MJ, Marin JJ.
Journal: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol (2009): 21
Authors: Herraez E, Macias RI, Vazquez-Tato J, Hierro C, Monte MJ, Marin JJ.
Journal: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol (2009): 21
Page updated on October 9, 2024