ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid FITC Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible*
ReadiLink™ xtra rapid antibody labeling kits require essentially only 2 simple mixing steps without a column purification needed. Specially formulated FITC used in this ReadiLink™ kit is quite stable and shows good reactivity and selectivity with antibodies. The kit has all the essential components for labeling ~2x50 ug antibody. Each of the two vials of specially formulated FITC dye provided in the kit is optimized for labeling ~50 µg antibody. ReadiLink™ xtra FITC rapid antibody labeling kit provides a convenient and robust method to label monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies with the green fluorescent FITC fluorophore. FITC is one of the most commonly used fluorophores for labeling antibodies. 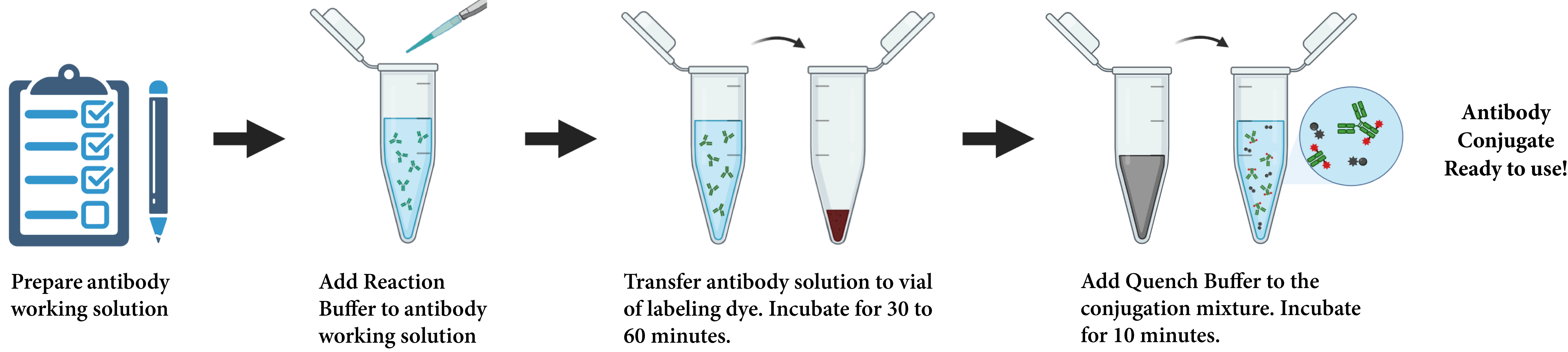

Figure 1. Overview of the ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid Antibody Labeling protocol. In just two simple steps, and with no purification necessary, covalently label microgram amounts of antibodies in under an hour.
Example protocol
AT A GLANCE
Important
Warm all the components and centrifuge the vials briefly before opening, and immediately prepare the required solutions before starting your conjugation. The following protocol is for recommendation.PREPARATION OF WORKING SOLUTION
Protein working solution (Solution A)
For labeling 50 µg of protein (assuming the target protein concentration is 1 mg/mL), mix 5 µL (10% of the total reaction volume) of Reaction Buffer (Component B) with 50 µL of the target protein solution.Note If you have a different protein concentration, adjust the protein volume accordingly to make ~50 µg of protein available for your labeling reaction.
Note For labeling 100 µg of protein (assuming the target protein concentration is 1 mg/mL), mix 10 µL (10% of the total reaction volume) of Reaction Buffer (Component B) with 100 µL of the target protein solution.
Note The protein should be dissolved in 1X phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2 - 7.4; if the protein is dissolved in glycine buffer, it must be dialyzed against 1X PBS, pH 7.2 - 7.4, or use Amicon Ultra-0.5, Ultracel-10 Membrane, 10 kDa (cat# UFC501008 from Millipore) to remove free amines or ammonium salts (such as ammonium sulfate and ammonium acetate) that are widely used for protein precipitation.
Note Impure antibodies or antibodies stabilized with bovine serum albumin (BSA) with 0.1 to 0.5 % will be labeled well.
Note For optimal labeling efficiency, a final protein concentration range of 1 - 2 mg/mL is recommended, with a significantly reduced conjugation efficiency at less than 1 mg/mL.
SAMPLE EXPERIMENTAL PROTOCOL
Run conjugation reaction
- Add the protein working solution (Solution A) to ONE vial of labeling dye (Component A), and mix them well by repeatedly pipetting for a few times or vortex the vial for a few seconds.
Note If labeling 100 µg of protein, use both vials (Component A) of labeling dye by dividing the 100 µg of protein into 2 x 50 µg of protein and reacting each 50 µg of protein with one vial of labeling dye. Then combine both vials for the next step. - Keep the conjugation reaction mixture at room temperature for 30 - 60 minutes.
Note The conjugation reaction mixture can be rotated or shaken for longer time if desired.
Stop Conjugation reaction
- Add 5 µL (for 50 µg protein) or 10 µL (for 100 µg protein) which is 10% of the total reaction volume of TQ™-Dyed Quench Buffer (Component C) into the conjugation reaction mixture; mix well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes. The labeled protein (antibody) is now ready to use.
Storage of Protein Conjugate
The protein conjugate should be stored at > 0.5 mg/mL in the presence of a carrier protein (e.g., 0.1% bovine serum albumin). For longer storage, the protein conjugates could be lyophilized or divided into single-used aliquots and stored at ≤ –20 °C.Spectrum
Product family
References
View all 50 references: Citation Explorer
Influence of Liver Intoxication by Carbon Tetrachloride or D-Galactosamine on Absorption of Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Dextran-10 and Other Marker Compounds with Different Molecular Weights from the Rat Liver Surface.
Authors: Miyamoto, Hirotaka and Tsuda, Kayoko and Honda, Tominori and Tokunaga, Ayako and Fumoto, Shintaro and Nishida, Koyo
Journal: Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin (2020): 319-324
Authors: Miyamoto, Hirotaka and Tsuda, Kayoko and Honda, Tominori and Tokunaga, Ayako and Fumoto, Shintaro and Nishida, Koyo
Journal: Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin (2020): 319-324
Fluorescein isothiocyanate and blue light irradiation alter cell-adhesiveness of cross-linked albumin films for cell patterning.
Authors: Tachibana, Akira and Iida, Atsuko and Tanabe, Toshizumi
Journal: Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry (2020): 800-803
Authors: Tachibana, Akira and Iida, Atsuko and Tanabe, Toshizumi
Journal: Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry (2020): 800-803
Electromembrane Extraction of Unconjugated Fluorescein Isothiocyanate from Solutions of Labeled Proteins Prior to Flow Induced Dispersion Analysis.
Authors: Restan, Magnus Saed and Pedersen, Morten E and Jensen, Henrik and Pedersen-Bjergaard, Stig
Journal: Analytical chemistry (2019): 6702-6708
Authors: Restan, Magnus Saed and Pedersen, Morten E and Jensen, Henrik and Pedersen-Bjergaard, Stig
Journal: Analytical chemistry (2019): 6702-6708
Highly Sensitive Measurement of Glomerular Permeability in Mice with Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-polysucrose 70.
Authors: Königshausen, Eva and Potthoff, Sebastian A and Woznowski, Magdalena and Stegbauer, Johannes and Rump, Lars C and Sellin, Lorenz
Journal: Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE (2019)
Authors: Königshausen, Eva and Potthoff, Sebastian A and Woznowski, Magdalena and Stegbauer, Johannes and Rump, Lars C and Sellin, Lorenz
Journal: Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE (2019)
Fluorescent property of glycol chitosan-fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugate for bio-imaging material.
Authors: Kim, Hee Cheol and Park, Won Ho
Journal: International journal of biological macromolecules (2019): 1217-1221
Authors: Kim, Hee Cheol and Park, Won Ho
Journal: International journal of biological macromolecules (2019): 1217-1221
Page updated on April 15, 2025



