ReadiLink™ Rapid mFluor™ Violet 420 Antibody Labeling Kit
Microscale Optimized for Labeling 50 μg Antibody Per Reaction
AAT Bioquest's mFluor™ dyes are developed for flow cytometry-focused applications. These dyes can be well excited by the laser lines of flow cytometers (e.g., 405 nm, 488 nm and 633 nm). mFluor™ Violet 420 dyes have fluorescence excitation and emission maxima of ~405 nm and ~420 nm respectively. These spectral characteristics make them an excellent replacement for Cascade® Blue labeling dye ( Cascade® Blue is the trademark of InvitroGen). mFluor™ Violet 420 SE is reasonably stable and shows good reactivity and selectivity with protein amino groups. This kit has all the essential components for labeling ~100 µg antibody with no column purification needed. mFluor™ Violet 420 SE antibody labeling kit provides a convenient method to label monoclonal, polyclonal antibodies or other proteins (>10 kDa) with the Violet Laser-excitable mFluor™ Violet 420 SE.
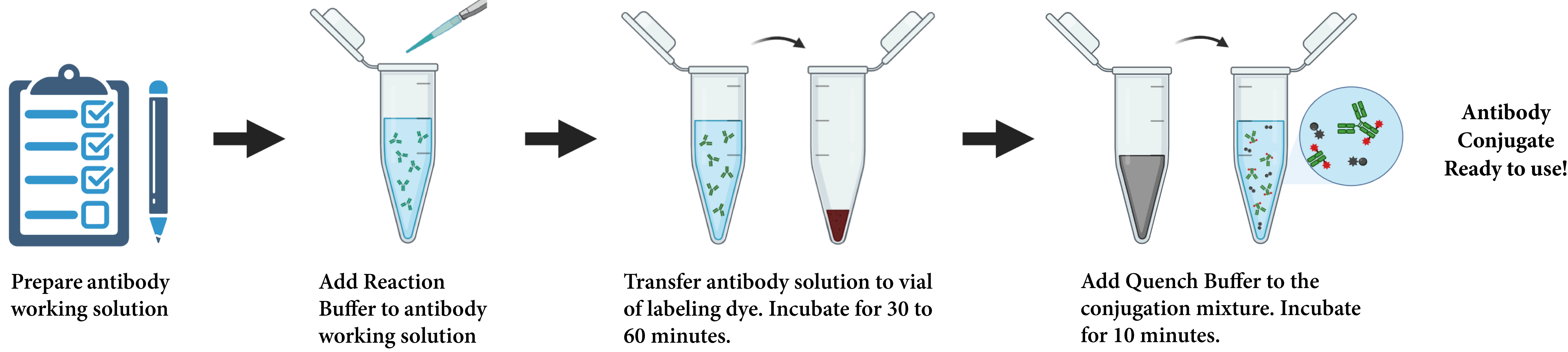
Figure 1. Overview of the ReadiLink™ Rapid Antibody Labeling protocol. In just two simple steps, and with no purification necessary, covalently label microgram amounts of antibodies in under an hour.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1105 | 2 Labelings | Price |
Spectral properties
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 37000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 403 |
| Emission (nm) | 427 |
| Quantum yield | 0.91 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 26, 2026

