Phalloidin Conjugates
iFluor® 488
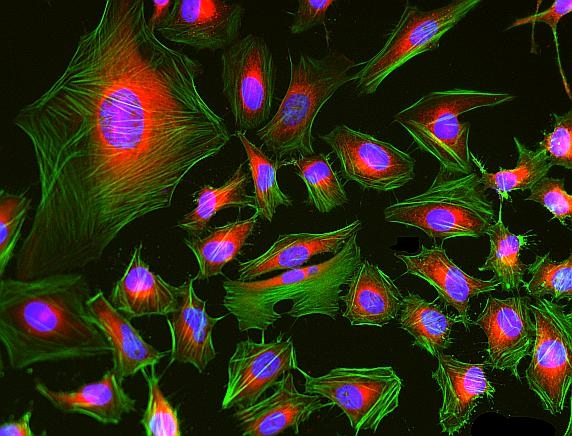
Phalloidin-iFluor® 488 Conjugate is an F-actin-specific probe with bright green fluorescence, enabling high-affinity visualization and quantification of filamentous actin in fixed and permeabilized cells.
- F-Actin Specific Binding: Bicyclic peptide binds between actin monomers (Kd ~20 nM)
- Superior Photostability: iFluor® 488 resists photobleaching better than FITC conjugates
- Fixed Cell Compatible: Withstands permeabilization and mounting procedures
- High-Resolution Imaging: Labels stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia structures

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23115 | 300 Tests | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | ~1400 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.21 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.11 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 75000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 491 |
| Emission (nm) | 516 |
| Quantum yield | 0.9 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H301, H311, H331 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R23, R24, R25 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 16, 2026

