ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 555 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible*
ReadiLink™ xtra rapid antibody labeling kits require essentially only 2 simple mixing steps without a column purification needed. Preactivated iFluor® 555 used in this ReadiLink™ kit is quite stable and shows good reactivity and selectivity with antibodies. The kit has all the essential components for labeling ~2x50 ug antibody. Each of the two vials of preactivated iFluor® 555 dye provided in the kit is optimized for labeling ~50 µg antibody. ReadiLink™ xtra iFluor® 555 rapid antibody labeling kit provides a convenient and robust method to label monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies with the bright red fluorescent iFluor® 555 fluorophore. AAT Bioquest's iFluor® dyes are optimized for labeling proteins, in particular, antibodies. These dyes are bright, photostable and have minimal quenching on proteins. They can be well excited by the major laser lines of fluorescence instruments (e.g., 350, 405, 488, 555 and 633 nm). 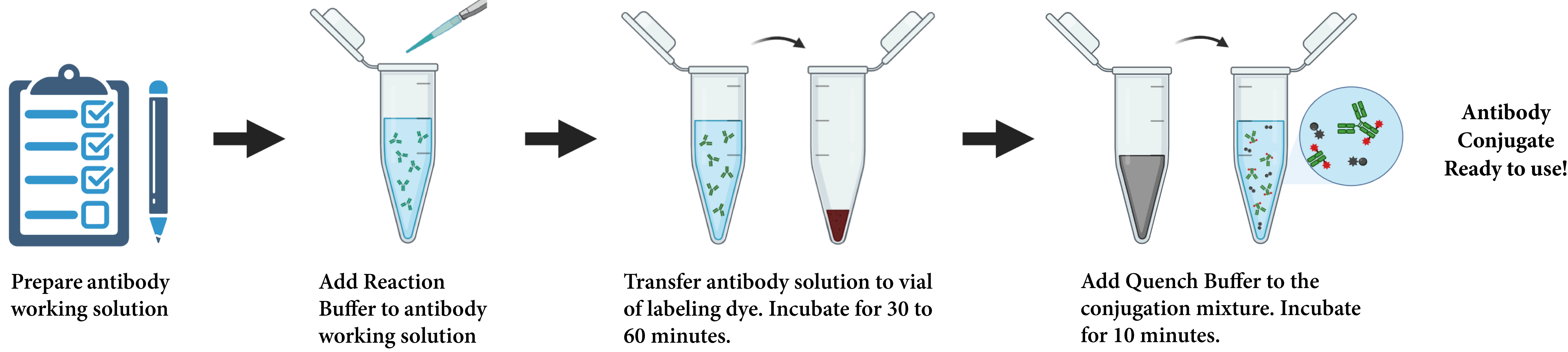

Figure 1. Overview of the ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid Antibody Labeling protocol. In just two simple steps, and with no purification necessary, covalently label microgram amounts of antibodies in under an hour.
Example protocol
AT A GLANCE
Important
Warm all the components and centrifuge the vials briefly before opening, and immediately prepare the required solutions before starting your conjugation. The following protocol is for recommendation.PREPARATION OF WORKING SOLUTION
Protein working solution (Solution A)
For labeling 50 µg of protein (assuming the target protein concentration is 1 mg/mL), mix 5 µL (10% of the total reaction volume) of Reaction Buffer (Component B) with 50 µL of the target protein solution.Note If you have a different protein concentration, adjust the protein volume accordingly to make ~50 µg of protein available for your labeling reaction.
Note For labeling 100 µg of protein (assuming the target protein concentration is 1 mg/mL), mix 10 µL (10% of the total reaction volume) of Reaction Buffer (Component B) with 100 µL of the target protein solution.
Note The protein should be dissolved in 1X phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2 - 7.4; if the protein is dissolved in glycine buffer, it must be dialyzed against 1X PBS, pH 7.2 - 7.4, or use Amicon Ultra-0.5, Ultracel-10 Membrane, 10 kDa (cat# UFC501008 from Millipore) to remove free amines or ammonium salts (such as ammonium sulfate and ammonium acetate) that are widely used for protein precipitation.
Note Impure antibodies or antibodies stabilized with bovine serum albumin (BSA) with 0.1 to 0.5 % will be labeled well.
Note For optimal labeling efficiency, a final protein concentration range of 1 - 2 mg/mL is recommended, with a significantly reduced conjugation efficiency at less than 1 mg/mL.
SAMPLE EXPERIMENTAL PROTOCOL
Run conjugation reaction
- Add the protein working solution (Solution A) to ONE vial of labeling dye (Component A), and mix them well by repeatedly pipetting for a few times or vortex the vial for a few seconds.
Note If labeling 100 µg of protein, use both vials (Component A) of labeling dye by dividing the 100 µg of protein into 2 x 50 µg of protein and reacting each 50 µg of protein with one vial of labeling dye. Then combine both vials for the next step. - Keep the conjugation reaction mixture at room temperature for 30 - 60 minutes.
Note The conjugation reaction mixture can be rotated or shaken for longer time if desired.
Stop Conjugation reaction
- Add 5 µL (for 50 µg protein) or 10 µL (for 100 µg protein) which is 10% of the total reaction volume of TQ™-Dyed Quench Buffer (Component C) into the conjugation reaction mixture; mix well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes. The labeled protein (antibody) is now ready to use.
Storage of Protein Conjugate
The protein conjugate should be stored at > 0.5 mg/mL in the presence of a carrier protein (e.g., 0.1% bovine serum albumin). For longer storage, the protein conjugates could be lyophilized or divided into single-used aliquots and stored at ≤ –20°C.Spectrum
Product family
| Name | Excitation (nm) | Emission (nm) | Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | Quantum yield | Correction Factor (260 nm) | Correction Factor (280 nm) |
| ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 350 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible* | 345 | 450 | 200001 | 0.951 | 0.83 | 0.23 |
| ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 488 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible* | 491 | 516 | 750001 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.11 |
| ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 594 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible* | 587 | 603 | 2000001 | 0.531 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 647 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible* | 656 | 670 | 2500001 | 0.251 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| ReadiLink™ xtra Rapid iFluor® 750 Antibody Labeling Kit *BSA-Compatible* | 757 | 779 | 2750001 | 0.121 | 0.044 | 0.039 |
References
View all 43 references: Citation Explorer
Cholinergic and adrenergic innervation of the pancreas in chinchilla (Chinchilla Laniger Molina).
Authors: Radzimirska, Malgorzata and Kuchinka, Jacek and Nowak, Elzbieta and Trybus, Wojciech and Szczurkowski, Aleksander
Journal: Folia histochemica et cytobiologica (2020): 54-60
Authors: Radzimirska, Malgorzata and Kuchinka, Jacek and Nowak, Elzbieta and Trybus, Wojciech and Szczurkowski, Aleksander
Journal: Folia histochemica et cytobiologica (2020): 54-60
When the air hits your brain: decreased arterial pulsatility after craniectomy leading to impaired glymphatic flow.
Authors: Plog, Benjamin A and Lou, Nanhong and Pierre, Clifford A and Cove, Alex and Kenney, H Mark and Hitomi, Emi and Kang, Hongyi and Iliff, Jeffrey J and Zeppenfeld, Douglas M and Nedergaard, Maiken and Vates, G Edward
Journal: Journal of neurosurgery (2019): 1-14
Authors: Plog, Benjamin A and Lou, Nanhong and Pierre, Clifford A and Cove, Alex and Kenney, H Mark and Hitomi, Emi and Kang, Hongyi and Iliff, Jeffrey J and Zeppenfeld, Douglas M and Nedergaard, Maiken and Vates, G Edward
Journal: Journal of neurosurgery (2019): 1-14
Efficient Long-Range, Directional Energy Transfer through DNA-Templated Dye Aggregates.
Authors: Zhou, Xu and Mandal, Sarthak and Jiang, Shuoxing and Lin, Su and Yang, Jianzhong and Liu, Yan and Whitten, David G and Woodbury, Neal W and Yan, Hao
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society (2019): 8473-8481
Authors: Zhou, Xu and Mandal, Sarthak and Jiang, Shuoxing and Lin, Su and Yang, Jianzhong and Liu, Yan and Whitten, David G and Woodbury, Neal W and Yan, Hao
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society (2019): 8473-8481
Intracerebroventricular Delivery of Recombinant NAMPT Deters Inflammation and Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia.
Authors: Chen, Fenghua and Weng, Zhongfang and Xia, Qinghai and Cao, Catherine and Leak, Rehana K and Han, Lihong and Xiao, Jian and Graham, Steven H and Cao, Guodong
Journal: Translational stroke research (2019): 719-728
Authors: Chen, Fenghua and Weng, Zhongfang and Xia, Qinghai and Cao, Catherine and Leak, Rehana K and Han, Lihong and Xiao, Jian and Graham, Steven H and Cao, Guodong
Journal: Translational stroke research (2019): 719-728
Enhanced broadband fluorescence detection of nucleic acids using multipolar gap-plasmons on biomimetic Au metasurfaces.
Authors: Narasimhan, Vinayak and Siddique, Radwanul Hasan and Hoffmann, Magnus and Kumar, Shailabh and Choo, Hyuck
Journal: Nanoscale (2019): 13750-13757
Authors: Narasimhan, Vinayak and Siddique, Radwanul Hasan and Hoffmann, Magnus and Kumar, Shailabh and Choo, Hyuck
Journal: Nanoscale (2019): 13750-13757
Page updated on April 15, 2025



