PG-cholesterylamine
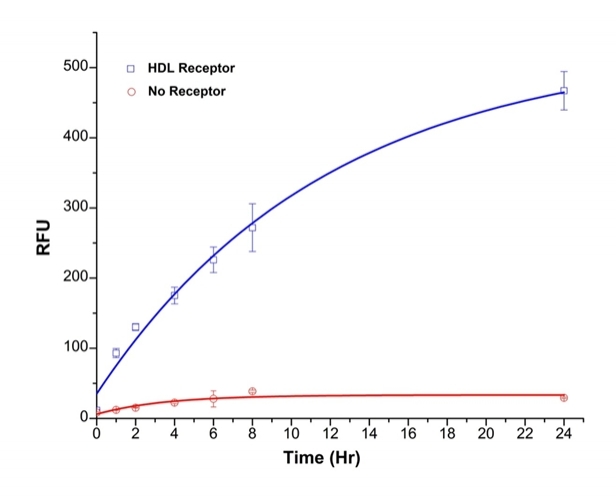
PG-cholesterylamine was reported by Zhang et al. to be an excellent fluorescent probe for monitoring cholesterol efflux. Reverse cholesterol transport is the process by which extrahepatic cells, including macrophage-derived foam cells in arterial atherosclerotic plaque, transport excessive cholesterol back to the liver for bile acid synthesis and excretion, thus lowering the peripheral lipid burden. PG-cholesterylamine is a derivative of N-alkyl-3β-cholesterylamine labeled with a fluorescein derivative, Pennsylvania Green (PG). Compared with the traditional radioisotope-based assay, this fluorescent probe gave similar results in the presence of known modulators of cholesterol efflux, such as cyclic AMP, and different cholesterol acceptors. When the fluorescent probe was employed in a high-throughput screening format, a variety of chemicals and bioactive compounds with known and unknown effects on cholesterol efflux could be tested simultaneously by plate-reader in a short period of time. Treatment of THP-1-derived macrophages with inhibitors of the membrane transporter ATP-binding cassette A1, such as glyburide or a specific antibody, significantly reduced the export of this fluorescent compound, indicating that ATP-binding cassette A1 represents the primary mediator of its cellular efflux. PG-cholesterylamine provides a safe, sensitive and reproducible alternative to radioactive assays in efflux experiments.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36700 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1043.73 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 487 |
| Correction factor (260 nm) | 0.32 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.35 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 80000 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 498 |
| Emission (nm) | 517 |
| Quantum yield | 0.7900 1 , 0.952 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
| CAS | 1264272-41-4 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 31, 2026

