Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent
200X DMSO Solution
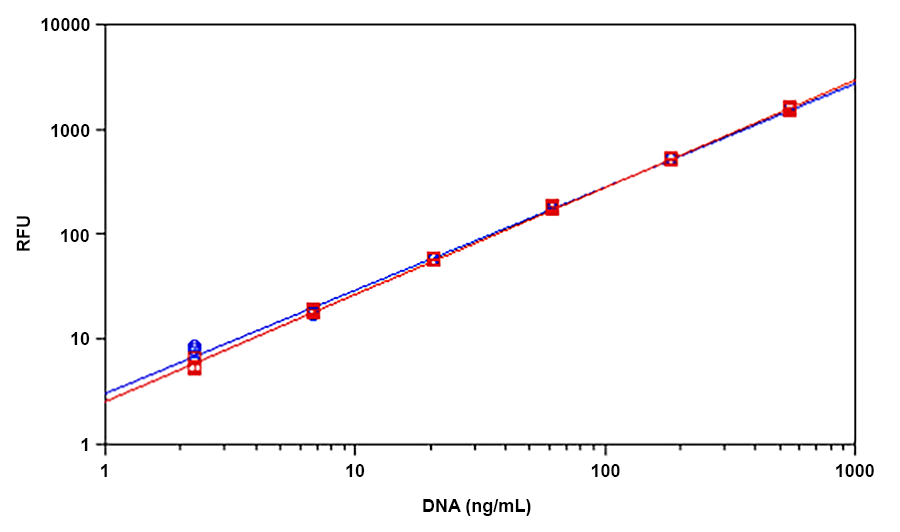
Helixyte™ Green is an excellent nucleic acid sensor that exhibits large fluorescence enhancement upon binding to dsDNA. It has the same spectral properties to those of PicoGreen®, thus a great replacement to PicoGreen® (PicoGreen® is the trademark of Invitrogen). The most commonly used technique for measuring nucleic acid concentration is the determination of absorbance at 260 nm (A260). However, the absorbance method suffers great interferences resulted from various contaminants commonly found in nucleic acid preparations, including nucleotides, single-stranded nucleic acids and proteins. Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent is an excellent alternative for quantifying DNAs with greatly improved sensitivity and selectivity. Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent is an ultra-sensitive fluorescent nucleic acid stain for quantitating double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in molecular biological procedures such as cDNA synthesis for library production and DNA fragment purification for subcloning, as well as diagnostic applications, such as quantitating DNA amplification products and primer extension assays. Using the Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent, you can selectively detect as little as 25 pg/ml of dsDNA in the presence of ssDNA, RNA, and free nucleotides. The assay is linear over three orders of magnitude and has little sequence dependence, allowing you to accurately measure DNA from many sources, including genomic DNA, viral DNA, miniprep DNA, or PCR amplification products. Helixyte™ Green dsDNA Quantifying Reagent has a few orders of magnitude more sensitive than the UV absorbance readings, saving on precious sample. It is specific for dsDNA in the presence of equimolar amounts of RNA.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17597 | 1 ml | Price | |
| 17598 | 10 ml | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 661.17 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 502 |
| Emission (nm) | 522 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H340 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R68 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 41116134 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 |
| Emission | 525 |
| Cutoff | 515 |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 19, 2026

