Cell Meter™ Live Cell TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit
Green Fluorescence
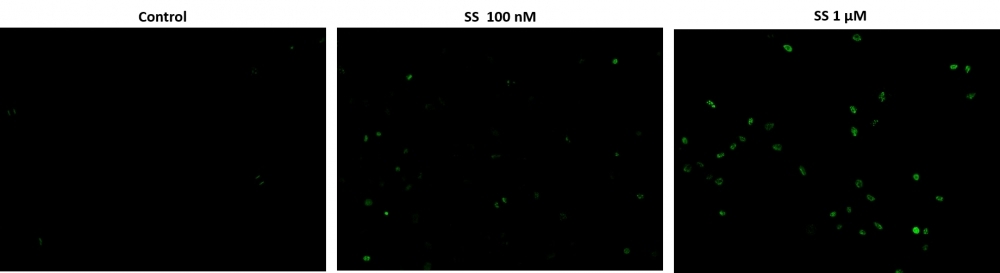
Cell Meter™ Live Cell TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit enables sensitive green-fluorescence-based detection of DNA fragmentation during apoptosis.
- Sodium cacodylate-free system: Eliminates toxic reagents found in conventional TUNEL kits, reducing false positives
- Direct detection: Incorporates fluorescent dUTPs into fragmented DNA without the need for antibodies
- Wide application range: Suitable for cancer research, drug toxicity studies, and disease-related apoptosis analysis
- Comparable alternative: Offers a safer, more direct workflow than BioVision’s (now Abcam) TUNEL apoptosis detection kits

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22849 | 50 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 498 |
| Emission (nm) | 522 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter |
| Emission | FITC filter |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm |
| Emission | 525 nm |
| Cutoff | 515 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on October 8, 2024

