Cell Meter™ Live Cell Caspase 3/7 and Phosphatidylserine Detection Kit
Triple Fluorescence Colors
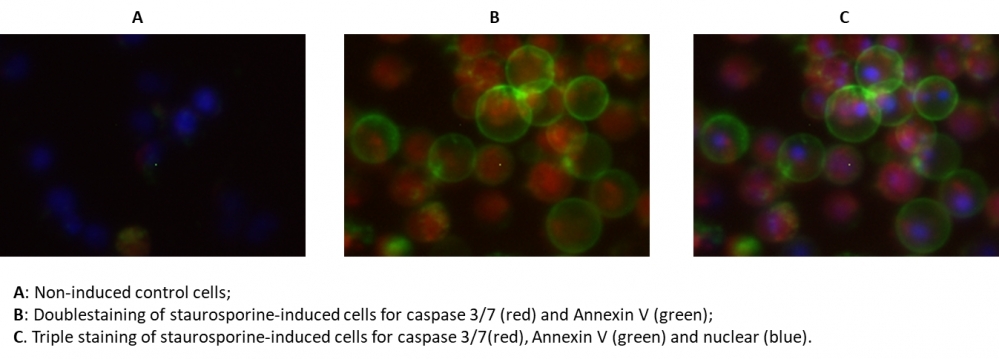
Our Cell Meter™ assay kits are a set of tools for monitoring cellular functions. In the process of apoptosis, one of key events is the activation of caspases. The activation of caspase 3/7 is an important for the initiation of apoptosis. It has been proven that caspase 3/7 has substrate selectivity for the peptide sequence Asp-Glu-Val-Asp (DEVD). This kit uses SR-DEVD-FMK as a fluorescent indicator to detect caspase 3/7 activities. SR-DEVD-FMK is cell permeable and nontoxic, once bound to caspases, the fluorescent reagent is retained inside the cell. The binding event prevents the caspases from further catalysis but will not stop apoptosis from proceeding. SR-DEVD-FMK is a red label reagent. Annexins are a family of proteins that bind to phospholipid membranes in the presence of calcium. Annexin V is used to detect apoptotic cells that express phosphatidylserine (PS) on the cell surface. The appearance of PS on the cell surface is a universal indicator of the initial/intermediate stages of cell apoptosis. Annexin V-dye conjugates monitor cell apoptosis through measuring the translocation of PS. The Annexin V-iFluor® 488™ used in this kit is a green labeling reagent, with Ex/Em = 490/525 nm. The kit is designed to detect apoptosis by simultaneously monitoring Caspase 3/7 and Annexin V activities in mammalian cells. The kit also provides a Hoechst dye for labeling the nucleus of the whole population of the cells, and propidium iodide dye for staining necrosis cells. This kit is applicable for fluorescence microscope, flow cytometer, and fluorescence microplate reader. The kit provides all the essential components with an optimized assay protocol.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22850 | 100 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm, 575/26 nm, 610/20 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC, PE, PE-Texas Red channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC channel for Annexin V-iFluor 488™, TRITC channel for TF3-DEVD-FMK, |
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm, 550 nm |
| Emission | 525 nm, 595 nm |
| Cutoff | 515 nm, 570 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 1, 2026
