Cell Meter™ JC-10 Mitochondrion Membrane Potential Assay Kit
Optimized for Microplate Assays
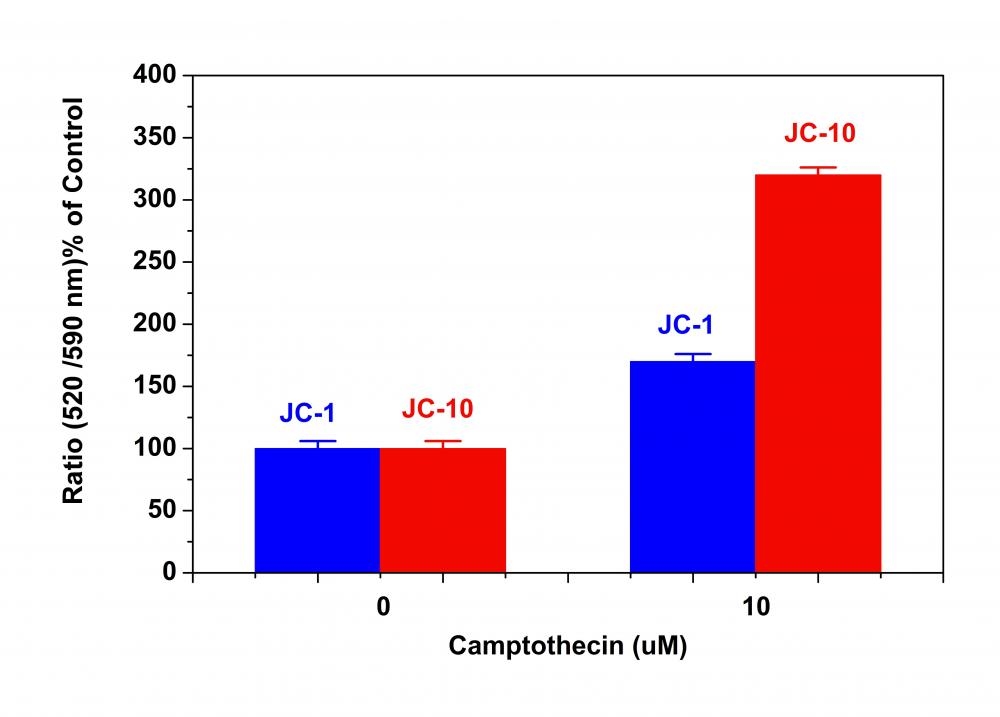
Although JC-1 is widely used in many labs, its poor water solubility makes it hard to use for some applications. Even at 1 µM concentration, JC-1 tends to precipitate in aqueous buffer. JC-10 has been developed to be a superior alternative to JC-1 where high dye concentration is desired. Compared to JC-1, our JC-10 has much better water solubility. JC-10 is capable of entering selectively into mitochondria, and changes reversibly its color from green to orange as membrane potentials increase. This property is due to the reversible formation of JC-10 aggregates upon membrane polarization that causes shifts in emitted light from 520 nm (i.e., emission of JC-10 monomeric form) to 570 nm (i.e., emission of J-aggregate). When excited at 490 nm, the color of JC-10 changes reversibly from green to greenish orange as the mitochondrial membrane becomes more polarized. This Cell Meter™ JC-10 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay Kit enable you to monitor mitochondrial membrane potential changes using a simple microplate reader while all the other commercial JC-1 assay kits require the use of a flow cytometer. Our kit provides the most robust method to monitor mitochondrial membrane potential changes, and can be readily used for screening a large compound library.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22800 | 500 Tests | Price |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 508 |
| Emission (nm) | 524 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490/540 nm |
| Emission | 525/590 nm |
| Cutoff | 515/570 nm |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Bottom read mode |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on February 7, 2026

