Cell Meter™ Fluorimetric Phagocytosis Assay Kit
Red Fluorescence
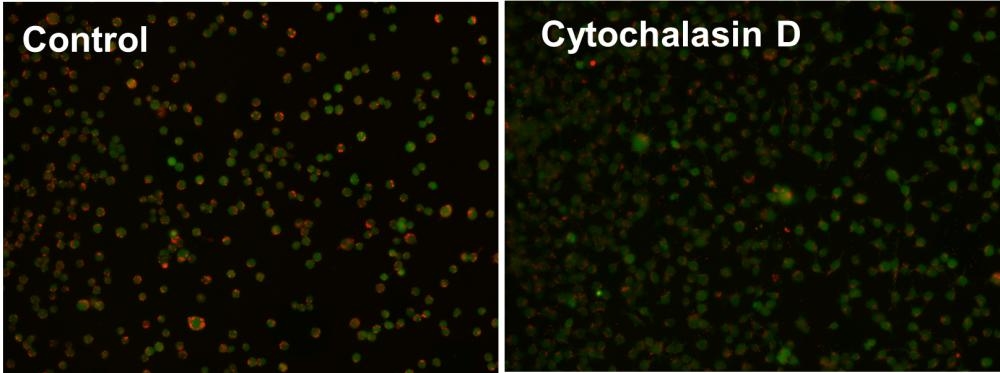
Cell Meter™ Fluorimetric Phagocytosis Assay Kit enables sensitive red-fluorescence-based detection of phagocytic activity in live cells.
- pH-activated fluorescence detection: Uses Protonex™ Red 600-latex beads that fluoresce only upon acidification in phagosomes
- Dual-color assay format: Includes a green viability dye to concurrently assess live cells and phagocytic function
- Wide application range: Ideal for studying innate immune responses, drug screening, and cell-based functional assays
- Comparable alternative: Provides a dual-fluorescence alternative to BioLegend’s Phagocytosis Detection Kit

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21225 | 100 Tests | Price |
Physical properties
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Excitation (nm) | 576 |
| Emission (nm) | 597 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
| Instrument specification(s) | Texas Red/FITC filter |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on January 28, 2026

