Annexin V, FITC Labeled
FITC Annexin V is a highly fluorescent conjugate used to identify and quantitate apoptotic cells by flow cytometry.
Product Description
Annexin V is a 35-36 kDa phospholipid-binding protein that has a high affinity for phosphatidylserine (PS) residues. In apoptotic cells, PS is translocated from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, making it accessible to Annexin V conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). By binding to PS, Annexin V FITC can be used to detect and quantify apoptotic cells via flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy.
Key Features
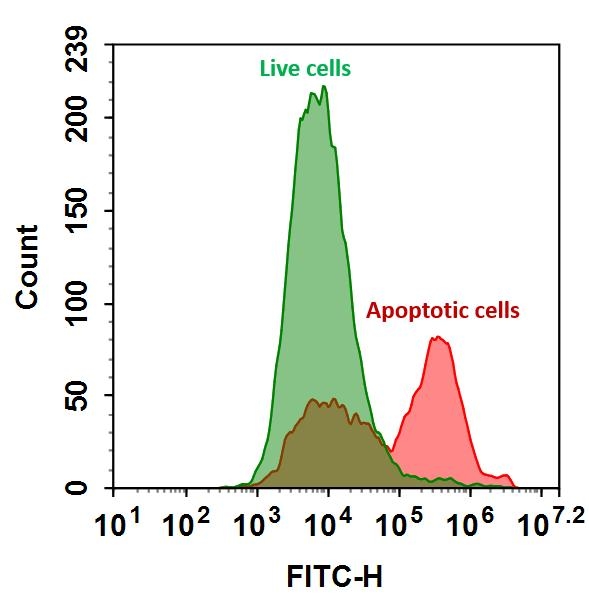
- High Sensitivity and Specificity to efficiently detect early apoptotic cells by binding to exposed PS.
- Dual Staining Capability can be used in conjunction with propidium iodide (PI) to distinguish between apoptotic and necrotic cells.
- Non-Radioactive Assay provides a safe and easy method for apoptosis detection without the need for radioactive materials.
- Rapid and Simple Protocol enables minimal hands-on time with straightforward staining and analysis procedures.
- Versatile Applications suitable for use in various cell types and experimental conditions.
Mechanism of Action
During apoptosis, the integrity of the plasma membrane changes, leading to the translocation of phosphatidylserine (PS) from the inner to the outer leaflet. Annexin V FITC, a fluorophore-conjugated protein with a high affinity for PS, selectively binds to the externalized PS residues. This binding event is detectable and quantifiable via flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy. The intensity of the FITC signal enables precise identification and quantification of apoptotic cells, as it directly correlates with Annexin V binding to PS on the cell surface.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20030 | 100 tests | Price | |
| 20032 | 300 tests | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | ~36000 |
| Solvent | Water |
Spectral properties
| Absorbance (nm) | 488 |
| Correction factor (280 nm) | 0.35 |
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 73000 |
| Excitation (nm) | 491 |
| Emission (nm) | 516 |
| Quantum yield | 0.92 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
Instrument settings
| Flow cytometer | |
| Excitation | 488 nm laser |
| Emission | 530/30 nm filter |
| Instrument specification(s) | FITC channel |
| Fluorescence microscope | |
| Excitation | FITC filter set |
| Emission | FITC filter set |
| Recommended plate | Black wall/clear bottom |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on October 8, 2024

