Amplite® Fluorimetric Glutathione GSH/GSSG Ratio Assay Kit
Green Fluorescence
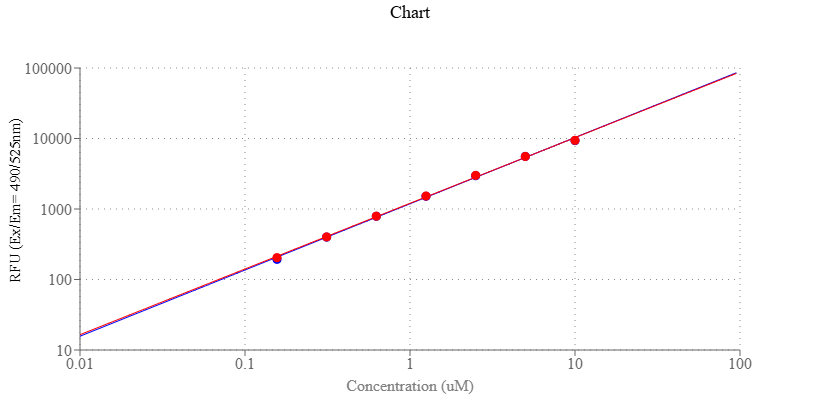
When cells are exposed to increased levels of oxidative stress, GSSG will accumulate and the ratio of GSH to GSSG will decrease. The glutathione redutase recycles GSSG to GSH with simultaneous oxidation of b-nicotinamide adenine dinuclecotide phosphate. The monitoring of GSH/GSSG ratio and the quantification of GSSG in biological samples are essential for evaluating the redox and detoxification status of cells and tissues in relation to the protective role of glutathione against oxidative and free-radical-mediated cell injury. There are a few reagents or assay kits available for the quantitation of thiols in biological systems. However, all the commercial kits either lack sensitivity or have tedious protocols. Our Amplite® Fluorimetric GSH/GSSG Ratio Kit provides an ultrasensitive assay to quantitate GSH in the sample. The kit uses a proprietary non-fluorescent dye that becomes strongly fluorescent upon reacting with thiol. The kit provides a sensitive, one-step fluorimetric method to detect as little as 1 picomole of cysteine or GSH in a 100 µL assay volume. The assay can be performed in a convenient 96-well or 384-well microtiter-plate format and easily adapted to automation without a separation step. Its signal can be easily read by a fluorescence microplate reader.

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10056 | 200 Tests | Price |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H333 |
| Hazard symbol | XN |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R22 |
| UNSPSC | 12171501 |
Instrument settings
| Fluorescence microplate reader | |
| Excitation | 490 nm |
| Emission | 520 nm |
| Cutoff | 510 nm |
| Recommended plate | Solid black |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on March 14, 2026
