7-AAD
7-Aminoactinomycin D; CAS 7240-37-1
7-AAD (7-aminoactinomycin D) is a cell-impermeant, G-C selective DNA intercalating dye with red fluorescence that specifically stains dead and necrotic cells for viability assessment in flow cytometry and microscopy.
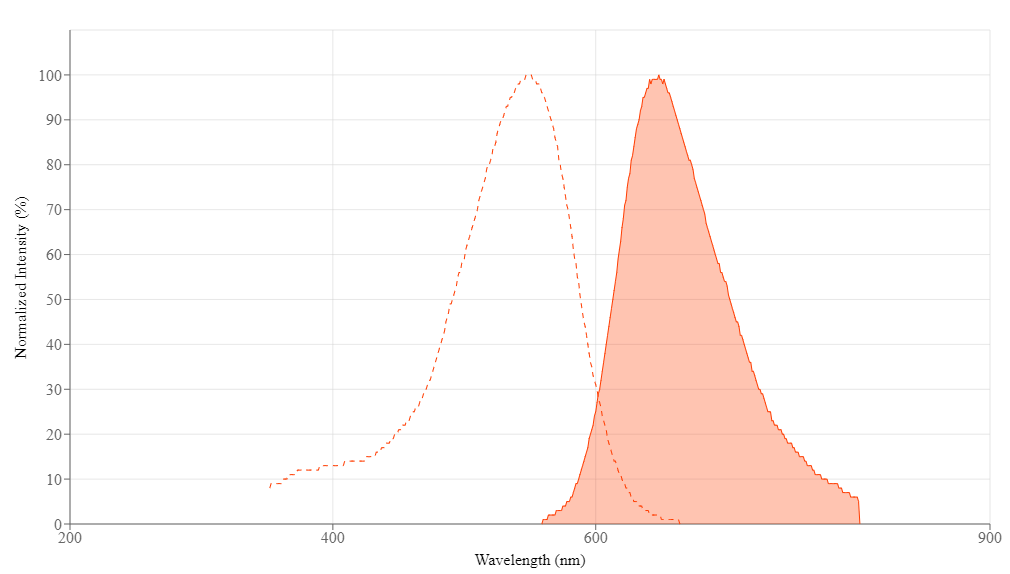
- G-C Selective DNA Intercalation: High affinity for GC-rich regions with red fluorescence (Ex/Em = 549/648 nm)
- Cell Impermeant Viability Dye: Specifically stains dead and necrotic cells with compromised membranes
- 488 nm Laser Compatible: Large Stokes shift reduces spectral overlap with FITC and PE in multicolor flow cytometry
- Lower Quantum Yield vs PI: QY = 0.02 provides controlled fluorescence intensity for sensitive detection

| Catalog | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17501 | 1 mg | Price |
Physical properties
| Molecular weight | 1270.43 |
| Solvent | DMSO |
Spectral properties
| Extinction coefficient (cm -1 M -1) | 27500 1 |
| Excitation (nm) | 549 |
| Emission (nm) | 648 |
| Quantum yield | 0.02 1 |
Storage, safety and handling
| H-phrase | H303, H313, H340 |
| Hazard symbol | T |
| Intended use | Research Use Only (RUO) |
| R-phrase | R20, R21, R68 |
| Storage | Freeze (< -15 °C); Minimize light exposure |
| UNSPSC | 41116134 |
| CAS | 7240-37-1 |
Contact us
| Telephone | |
| Fax | |
| sales@aatbio.com | |
| International | See distributors |
| Bulk request | Inquire |
| Custom size | Inquire |
| Technical Support | Contact us |
| Request quotation | Request |
| Purchase order | Send to sales@aatbio.com |
| Shipping | Standard overnight for United States, inquire for international |
Page updated on September 24, 2024

